Product Description
dc 12v trolling motor small planet worm gear dc motor 12v 30w industrial manfactorer
Application of 12 V DC Motor
12 V DC motors are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Fans: 12 V DC motors are used in fans to provide ventilation.
- Pumps: 12 V DC motors are used in pumps to circulate fluids.
- Winches: 12 V DC motors are used in winches to pull loads.
- Door openers: 12 V DC motors are used in door openers to open and close doors.
- Toys: 12 V DC motors are used in toys to provide movement.
- Robotics: 12 V DC motors are used in robotics to provide movement.
- Electric vehicles: 12 V DC motors are used in electric vehicles to provide propulsion.
12 V DC motors are a versatile type of motor that can be used in a wide variety of applications. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to find, making them a popular choice for many projects.
Here are some of the advantages of using 12 V DC motors:
- Inexpensive: 12 V DC motors are relatively inexpensive, making them a cost-effective option for many projects.
- Easy to find: 12 V DC motors are widely available, making them easy to find and purchase.
- Versatile: 12 V DC motors can be used in a wide variety of applications, making them a versatile choice for many projects.
- Reliable: 12 V DC motors are typically reliable and durable, making them a good choice for long-term use.
Here are some of the disadvantages of using 12 V DC motors:
- Low power: 12 V DC motors typically have lower power than other types of motors, making them less suitable for applications that require high power.
- Low speed: 12 V DC motors typically have lower speeds than other types of motors, making them less suitable for applications that require high speed.
- Noise: 12 V DC motors can be noisy, making them less suitable for applications where noise is a concern.
Overall, 12 V DC motors are a versatile and reliable type of motor that can be used in a wide variety of applications. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to find, making them a popular choice for many projects.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | High Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 12 |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

How does the speed control of a DC motor work, and what methods are commonly employed?
The speed control of a DC (Direct Current) motor is essential for achieving precise control over its rotational speed. Various methods can be employed to regulate the speed of a DC motor, depending on the specific application requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of how speed control of a DC motor works and the commonly employed methods:
1. Voltage Control:
One of the simplest methods to control the speed of a DC motor is by varying the applied voltage. By adjusting the voltage supplied to the motor, the electromotive force (EMF) induced in the armature windings can be controlled. According to the principle of electromagnetic induction, the speed of the motor is inversely proportional to the applied voltage. Therefore, reducing the voltage decreases the speed, while increasing the voltage increases the speed. This method is commonly used in applications where a simple and inexpensive speed control mechanism is required.
2. Armature Resistance Control:
Another method to control the speed of a DC motor is by varying the armature resistance. By inserting an external resistance in series with the armature windings, the total resistance in the circuit increases. This increase in resistance reduces the armature current, thereby reducing the motor’s speed. Conversely, reducing the resistance increases the armature current and the motor’s speed. However, this method results in significant power loss and reduced motor efficiency due to the dissipation of excess energy as heat in the external resistance.
3. Field Flux Control:
Speed control can also be achieved by controlling the magnetic field strength of the motor’s stator. By altering the field flux, the interaction between the armature current and the magnetic field changes, affecting the motor’s speed. This method can be accomplished by adjusting the field current through the field windings using a field rheostat or by employing a separate power supply for the field windings. By increasing or decreasing the field flux, the speed of the motor can be adjusted accordingly. This method offers good speed regulation and efficiency but requires additional control circuitry.
4. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM):
Pulse Width Modulation is a widely used technique for speed control in DC motors. It involves rapidly switching the applied voltage on and off at a high frequency. The duty cycle, which represents the percentage of time the voltage is on, is varied to control the effective voltage applied to the motor. By adjusting the duty cycle, the average voltage across the motor is modified, thereby controlling its speed. PWM provides precise speed control, high efficiency, and low power dissipation. It is commonly employed in applications such as robotics, industrial automation, and electric vehicles.
5. Closed-Loop Control:
In closed-loop control systems, feedback from the motor’s speed or other relevant parameters is used to regulate the speed. Sensors such as encoders or tachometers measure the motor’s actual speed, which is compared to the desired speed. The difference, known as the error signal, is fed into a control algorithm that adjusts the motor’s input voltage or other control parameters to minimize the error and maintain the desired speed. Closed-loop control provides excellent speed regulation and accuracy, making it suitable for applications that require precise speed control, such as robotics and CNC machines.
These methods of speed control provide flexibility and adaptability to various applications, allowing DC motors to be effectively utilized in a wide range of industries and systems.

How do DC motors compare to AC motors in terms of performance and efficiency?
When comparing DC (Direct Current) motors and AC (Alternating Current) motors, several factors come into play, including performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how DC motors and AC motors compare in terms of performance and efficiency:
1. Performance:
Speed Control: DC motors typically offer better speed control compared to AC motors. DC motors can be easily controlled by varying the voltage applied to the armature, allowing for precise and smooth speed regulation. On the other hand, AC motors rely on complex control methods such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) to achieve speed control, which can be more challenging and costly.
Starting Torque: DC motors generally provide higher starting torque compared to AC motors. The presence of a separate field winding in DC motors allows for independent control of the field current, enabling higher torque during motor startup. AC motors, especially induction motors, typically have lower starting torque, requiring additional starting mechanisms or devices.
Reversibility: DC motors offer inherent reversibility, meaning they can easily change their rotational direction by reversing the polarity of the applied voltage. AC motors, particularly induction motors, require more complex control mechanisms to achieve reversible operation.
Dynamic Response: DC motors have faster dynamic response characteristics compared to AC motors. They can quickly accelerate or decelerate, making them suitable for applications that require rapid changes in speed or precise control, such as robotics or servo systems.
2. Efficiency:
Full Load Efficiency: AC motors, especially three-phase induction motors, generally exhibit higher full load efficiencies compared to DC motors. This efficiency advantage is primarily due to the absence of commutation and the use of a rotating magnetic field in AC motors, which results in reduced energy losses and improved efficiency.
Partial Load Efficiency: DC motors can have higher efficiency at partial loads compared to AC motors. DC motors can be controlled by adjusting the armature voltage, allowing them to operate at reduced power while maintaining relatively high efficiency. AC motors, especially induction motors, may experience reduced efficiency at partial loads due to factors such as increased iron losses and reduced power factor.
Regenerative Braking: DC motors offer the advantage of regenerative braking, where the motor acts as a generator and converts kinetic energy into electrical energy during deceleration or braking. This regenerative braking capability allows for energy recovery, increasing overall system efficiency. AC motors typically require additional components or systems to achieve regenerative braking.
Power Factor: AC motors, when properly designed and operated, can have a power factor close to unity. This means that they draw relatively low reactive power from the electrical grid, resulting in improved power system efficiency. DC motors, on the other hand, may exhibit a lower power factor and require power factor correction measures if necessary.
In summary, DC motors and AC motors have their respective strengths and weaknesses in terms of performance and efficiency. DC motors excel in speed control, starting torque, reversibility, and dynamic response. AC motors, particularly three-phase induction motors, generally offer higher full load efficiency and power factor. However, DC motors can achieve higher efficiency at partial loads and have the advantage of regenerative braking. The choice between DC motors and AC motors depends on the specific application requirements, cost considerations, and the desired balance between performance and efficiency.

Are there innovations or emerging technologies in the field of DC motor design?
Yes, there have been several innovations and emerging technologies in the field of DC (Direct Current) motor design. These advancements aim to improve the performance, efficiency, reliability, and overall capabilities of DC motors. Here’s a detailed explanation of some notable innovations and emerging technologies in DC motor design:
1. Brushless DC Motors:
One significant advancement in DC motor design is the development and widespread adoption of brushless DC motors (BLDC motors). Unlike traditional DC motors that use brushes for commutation, BLDC motors employ electronic commutation through the use of permanent magnets and motor controller circuits. This eliminates the need for brushes, reducing maintenance requirements and improving overall motor efficiency and lifespan. BLDC motors offer higher torque density, smoother operation, better speed control, and improved energy efficiency compared to conventional brushed DC motors.
2. High-Efficiency Materials:
The use of high-efficiency materials in DC motor design has been an area of focus for improving motor performance. Advanced magnetic materials, such as neodymium magnets, have allowed for stronger and more compact motor designs. These materials increase the motor’s power density, enabling higher torque output and improved efficiency. Additionally, advancements in materials used for motor windings and core laminations have reduced electrical losses and improved overall motor efficiency.
3. Power Electronics and Motor Controllers:
Advancements in power electronics and motor control technologies have greatly influenced DC motor design. The development of sophisticated motor controllers and efficient power electronic devices enables precise control of motor speed, torque, and direction. These technologies have resulted in more efficient and reliable motor operation, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced motor performance in various applications.
4. Integrated Motor Systems:
Integrated motor systems combine the motor, motor controller, and associated electronics into a single unit. These integrated systems offer compact designs, simplified installation, and improved overall performance. By integrating the motor and controller, issues related to compatibility and communication between separate components are minimized. Integrated motor systems are commonly used in applications such as robotics, electric vehicles, and industrial automation.
5. IoT and Connectivity:
The integration of DC motors with Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and connectivity has opened up new possibilities for monitoring, control, and optimization of motor performance. By incorporating sensors, actuators, and connectivity features, DC motors can be remotely monitored, diagnosed, and controlled. This enables predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and real-time performance adjustments, leading to improved efficiency and reliability in various applications.
6. Advanced Motor Control Algorithms:
Advanced motor control algorithms, such as sensorless control and field-oriented control (FOC), have contributed to improved performance and efficiency of DC motors. Sensorless control techniques eliminate the need for additional sensors by leveraging motor current and voltage measurements to estimate rotor position. FOC algorithms optimize motor control by aligning the magnetic field with the rotor position, resulting in improved torque and efficiency, especially at low speeds.
These innovations and emerging technologies in DC motor design have revolutionized the capabilities and performance of DC motors. Brushless DC motors, high-efficiency materials, advanced motor control techniques, integrated motor systems, IoT connectivity, and advanced control algorithms have collectively contributed to more efficient, reliable, and versatile DC motor solutions across various industries and applications.


editor by CX 2024-04-26
China manufacturer DC Electric 12V 24V 30W 80rpm 63mm Worm Gear Motor wiper Motor with high quality
Product Description
| voltage VDC |
no load speed RPM |
no load current A |
load torque KG.CM |
on load speed RPM |
power W |
ratio |
| 12 | 80 | 1.8 | 60 | 68 | 80 | 60:1 |
| 12 | 130 | 1.2 | 33 | 110 | 30 | 20:1 |
| 12 | 150 | 1.2 | 45 | 130 | 30 | 20:1 |
| 12 | 170 | 1.4 | 35 | 150 | 45 | 24:1 |
| 24 | 30 | 1.4 | 60 | 25 | 30 | 60:1 |
| 24 | 65 | 120 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 20:1 |
| 24 | 210 | 1.0 | 40 | 180 | 45 | 75:1 |
technical feature High Power version with 50A stall current:
With 48CPR encoder or not 48CPR
With back shaft or not.
With metal brush or carbon brush.
76mm dc worm gear motor
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Worm Gear Motor |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Low Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Open Type |
| Number of Poles: | 2 |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What is a DC motor, and how does it differ from other types of electric motors?
A DC (Direct Current) motor is an electric motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. It operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction and the interaction between current-carrying conductors and magnetic fields. DC motors are widely used in various applications due to their simplicity, controllability, and versatility. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a DC motor is and how it differs from other types of electric motors:
1. Basic Operation:
In a DC motor, electrical energy is supplied to the motor’s armature through a DC power source, typically a battery or a rectified power supply. The armature consists of multiple coils or windings that are evenly spaced around the motor’s rotor. The rotor is a cylindrical core with a shaft that rotates when the motor is energized. When current flows through the armature windings, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the fixed magnetic field produced by the motor’s stator. This interaction generates a torque, causing the rotor to rotate.
2. Commutation:
DC motors employ a commutator and brushes for the conversion of electrical energy and the rotation of the rotor. The commutator consists of a segmented cylindrical ring attached to the rotor shaft, and the brushes are stationary conductive contacts that make contact with the commutator segments. As the rotor spins, the brushes maintain contact with the commutator segments, periodically reversing the direction of the current flow in the armature windings. This reversal of current flow in the armature windings ensures continuous rotation of the rotor in the same direction.
3. Types of DC Motors:
DC motors can be classified into different types based on their construction and the method of field excitation. The two main types are:
- Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors have a mechanical commutator and brushes to switch the current direction in the armature windings. These motors are relatively simple, cost-effective, and offer good torque characteristics. However, the commutator and brushes require regular maintenance and can generate electrical noise and brush wear debris.
- Brushless DC Motors (BLDC): Brushless DC motors, also known as electronically commutated motors (ECMs), use electronic circuits and sensors to control the current flow in the motor windings. They eliminate the need for brushes and commutators, resulting in reduced maintenance and improved reliability. BLDC motors offer higher efficiency, smoother operation, and better speed control compared to brushed DC motors.
4. Speed Control:
DC motors provide excellent speed control capabilities. By adjusting the voltage applied to the motor, the speed of the DC motor can be regulated. Lowering the voltage reduces the motor’s speed, while increasing the voltage increases the speed. This feature makes DC motors suitable for applications that require precise speed control, such as robotics, conveyor systems, and electric vehicles.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages:
DC motors have several advantages, including:
- Simple construction and easy maintenance (for brushed DC motors).
- High starting torque.
- Precise speed control.
- Good controllability over a wide range of loads.
However, DC motors also have some limitations, such as:
- Brushed DC motors require periodic maintenance and have limited brush life.
- Brushed DC motors can generate electrical noise.
- Brushless DC motors are often more expensive compared to brushed DC motors.
6. Differences from Other Electric Motors:
DC motors differ from other types of electric motors, such as AC (Alternating Current) motors, in several ways:
- Power Source: DC motors require a DC power source, while AC motors operate from an AC power supply.
- Speed Control: DC motors offer precise speed control by adjusting the applied voltage, whereas AC motors typically rely on frequency control for speed regulation.
- Construction: DC motors use a commutator and brushes (in brushed DC motors) or electronic commutation (in brushless DC motors), while AC motors do not require commutation.
- Starting Torque: DC motors typically provide higher starting torque compared to AC motors.
Overall, DC motors are versatile and widely used in various applications due to their controllability, speed regulation capabilities, and simplicity. The advancements inpower electronics and motor control technologies have further enhanced the performance and efficiency of DC motors, making them a popular choice in many industries.
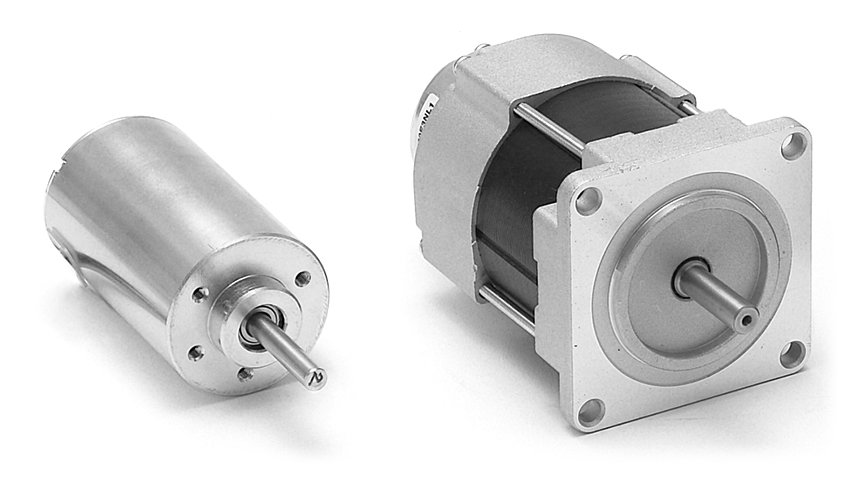
Are there specific types of DC motors designed for different industries or applications?
Yes, there are specific types of DC (Direct Current) motors that are designed and optimized for various industries and applications. DC motors offer a wide range of performance characteristics, allowing them to be tailored to specific requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of the types of DC motors designed for different industries or applications:
1. Brushed DC Motors:
Brushed DC motors are commonly used in applications that require simple and cost-effective motor solutions. They are suitable for applications with lower efficiency requirements and where maintenance considerations are manageable. Some common industries and applications that use brushed DC motors include:
- Automotive: Power window mechanisms, windshield wipers, cooling fans, and seat adjustment systems.
- Consumer Electronics: Household appliances, toys, power tools, and personal care devices.
- Industrial Machinery: Conveyors, pumps, fans, and machine tools.
2. Brushless DC Motors:
Brushless DC motors are known for their higher efficiency, greater reliability, and precise control capabilities. They are widely used in industries and applications that demand higher performance and advanced control features. Some specific industries and applications that utilize brushless DC motors include:
- Automotive: Electric power steering systems, electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and HVAC systems.
- Aerospace and Defense: Actuators, robotics, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and missile systems.
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment: Centrifuges, pumps, robotics, and diagnostic devices.
- Industrial Automation: CNC machines, robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and precision motion control systems.
- Renewable Energy: Wind turbine generators, solar tracking systems, and energy storage systems.
3. High-Torque DC Motors:
High-torque DC motors are designed to provide substantial torque output at low speeds. They are commonly used in applications that require heavy lifting or high starting torque. Industries and applications that often utilize high-torque DC motors include:
- Material Handling: Cranes, hoists, winches, lifts, and elevators.
- Construction and Mining: Excavators, bulldozers, drilling rigs, and conveyor systems.
- Automotive: Electric vehicles, electric powertrains, and traction control systems.
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Thrusters, winches, and anchor handling systems.
4. Low-Voltage DC Motors:
Low-voltage DC motors are designed to operate at lower voltages, typically below 24 volts. They are commonly used in battery-powered applications and systems where safety or specific voltage requirements exist. Some industries and applications that utilize low-voltage DC motors include:
- Automotive: Automotive accessories, window actuators, and door locks.
- Robotics and Hobbyist Projects: DIY robots, RC vehicles, and model trains.
- Solar Power Systems: Solar tracking systems, solar panel actuators, and solar-powered water pumps.
- Home Automation: Automated blinds, curtains, and smart home devices.
These are just a few examples of the types of DC motors designed for different industries and applications. The versatility and adaptability of DC motors make them suitable for a wide range of uses, and manufacturers often offer customized motor solutions to meet specific requirements.

How does the size and power rating of a DC motor affect its suitability for different tasks?
The size and power rating of a DC (Direct Current) motor play crucial roles in determining its suitability for different tasks and applications. The size and power rating directly impact the motor’s performance characteristics, including its torque output, speed range, efficiency, and overall capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the size and power rating of a DC motor affect its suitability for different tasks:
Size of DC Motor:
The size of a DC motor refers to its physical dimensions, including its diameter, length, and overall volume. The size of the motor influences its ability to fit into specific spaces or applications with space constraints. Here are some key considerations regarding the size of a DC motor:
1. Space Limitations: In applications where space is limited, such as small robotic systems or compact machinery, smaller-sized DC motors are preferred. These motors provide a more convenient and efficient integration into the overall system design.
2. Weight Constraints: Certain applications, such as drones or lightweight robots, may have strict weight limitations. Smaller-sized DC motors are generally lighter, making them more suitable for weight-sensitive tasks where minimizing the overall system weight is essential.
3. Cooling and Heat Dissipation: The size of a DC motor can impact its ability to dissipate heat generated during operation. Smaller-sized motors may have less surface area for heat dissipation, which can lead to increased operating temperatures. In contrast, larger-sized motors typically have better heat dissipation capabilities, allowing for sustained operation under heavy loads or in high-temperature environments.
Power Rating of DC Motor:
The power rating of a DC motor refers to the maximum power it can deliver or the power it consumes during operation. The power rating determines the motor’s capacity to perform work and influences its performance characteristics. Here are some key considerations regarding the power rating of a DC motor:
1. Torque Output: The power rating of a DC motor is directly related to its torque output. Higher power-rated motors generally provide higher torque, allowing them to handle more demanding tasks or applications that require greater force or load capacity. For example, heavy-duty industrial machinery or electric vehicles often require DC motors with higher power ratings to generate sufficient torque for their intended tasks.
2. Speed Range: The power rating of a DC motor affects its speed range capabilities. Motors with higher power ratings can typically achieve higher speeds, making them suitable for applications that require rapid or high-speed operation. On the other hand, lower power-rated motors may have limited speed ranges, making them more suitable for applications that require slower or controlled movements.
3. Efficiency: The power rating of a DC motor can impact its efficiency. Higher power-rated motors tend to have better efficiency, meaning they can convert a larger proportion of electrical input power into mechanical output power. Increased efficiency is desirable in applications where energy efficiency or battery life is a critical factor, such as electric vehicles or portable devices.
4. Overload Capability: The power rating of a DC motor determines its ability to handle overloads or sudden changes in load conditions. Motors with higher power ratings generally have a greater overload capacity, allowing them to handle temporary load spikes without stalling or overheating. This characteristic is crucial in applications where intermittent or varying loads are common.
Overall, the size and power rating of a DC motor are important factors in determining its suitability for different tasks. Smaller-sized motors are advantageous in space-constrained or weight-sensitive applications, while larger-sized motors offer better heat dissipation and can handle heavier loads. Higher power-rated motors provide greater torque, speed range, efficiency, and overload capability, making them suitable for more demanding tasks. It is crucial to carefully consider the specific requirements of the application and choose a DC motor size and power rating that aligns with those requirements to ensure optimal performance and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-04-03
China Custom High Torque 12V 24V Micro DC Wiper Worm Gear Motor 12 24 Volt Automatic Electric Garage Sliding Gate Door Opener Brush DC Motor vacuum pump distributors
Product Description
High Torque 12V 24V Micro Dc Wiper Worm Gear Motor 12 24 Volt Automatic Electric Garage Sliding Gate Door Opener Brush Dc Motor
1)Product Description:
1°size:Diameter 59mm
2°lifespan:5000 hours
3°gear material: plastic or brass
4°IP rate:IP54
2)Complete Specification:
3)Motor Drawing:
Shaft drawing:
4)Application:
welding machine, electrical household, CHINAMFG machinery, office intelligent equipment, hotel leisure, antomated machine and so on.
Motor Voltage: DC12V, 24V,42V,48V,90V,110V ,300V
Motor Rated Power:15W, 25W,30W,45W,65W, 95W,120W,150W,180W
Motor no-load Speed:15RPM, 30RPM,60RPM,80RM,120RPM,150RPM,180RPM,200RPM,220RPM.
5)Factory show:
Transfer way:
7)RFQ:
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
A: We are Integration of industry and trade, with over 20 years experience in DC worm gear motor. Our company have accumulated skilled production line, complete management and powerful research support, which could match all of the customers’ requirements and make them satisfaction.
Q: What is your main product?
– DC Motor: Gear motor, Square motor, Stepped motor, and Micro motor
-Welding equipment: Wire feeder, Welding rod, Welding Torch, Earth clamp, Electrode holder, and Rectifier
Q: What if I don’t know which DC motor I need?
A: Don’t worry, Send as much information as you can, our team will help you find the right 1 you are looking for.
Q: What is your terms of payment ?
A: Payment=1000USD, 30% T/T in advance ,balance before shippment.
If you have another question, pls feel free to contact us as below:
Q: How to delivery:
A: By sea – Buyer appoint forwarder, or our sales team find suitable forwarder for buyers.
By air – Buyer offer collect express account, or our sales team find suitable express for buyers. (Mostly for sample)
Others – Actually,samples send by DHL,UPS, TNT and Fedex etc. We arrange to delivery goods to some place from China appointed by buyers.
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: Generally it is 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-20 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How is the efficiency of a gear motor measured, and what factors can affect it?
The efficiency of a gear motor is a measure of how effectively it converts electrical input power into mechanical output power. It indicates the motor’s ability to minimize losses and maximize its energy conversion efficiency. The efficiency of a gear motor is typically measured using specific methods, and several factors can influence it. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Measuring Efficiency:
The efficiency of a gear motor is commonly measured by comparing the mechanical output power (Pout) to the electrical input power (Pin). The formula to calculate efficiency is:
Efficiency = (Pout / Pin) * 100%
The mechanical output power can be determined by measuring the torque (T) produced by the motor and the rotational speed (ω) at which it operates. The formula for mechanical power is:
Pout = T * ω
The electrical input power can be measured by monitoring the current (I) and voltage (V) supplied to the motor. The formula for electrical power is:
Pin = V * I
By substituting these values into the efficiency formula, the efficiency of the gear motor can be calculated as a percentage.
Factors Affecting Efficiency:
Several factors can influence the efficiency of a gear motor. Here are some notable factors:
- Friction and Mechanical Losses: Friction between moving parts, such as gears and bearings, can result in mechanical losses and reduce the overall efficiency of the gear motor. Minimizing friction through proper lubrication, high-quality components, and efficient design can help improve efficiency.
- Gearing Efficiency: The design and quality of the gears used in the gear motor can impact its efficiency. Gear trains can introduce mechanical losses due to gear meshing, misalignment, or backlash. Using well-designed gears with proper tooth profiles and minimizing gear train losses can improve efficiency.
- Motor Type and Construction: Different types of motors (e.g., brushed DC, brushless DC, AC induction) have varying efficiency characteristics. Motor construction, such as the quality of magnetic materials, winding resistance, and rotor design, can also affect efficiency. Choosing motors with higher efficiency ratings can improve overall gear motor efficiency.
- Electrical Losses: Electrical losses, such as resistive losses in motor windings or in the motor drive circuitry, can reduce efficiency. Minimizing resistance, optimizing motor drive electronics, and using efficient control algorithms can help mitigate electrical losses.
- Load Conditions: The operating conditions and load characteristics placed on the gear motor can impact its efficiency. Heavy loads, high speeds, or frequent acceleration and deceleration can increase losses and reduce efficiency. Matching the gear motor’s specifications to the application requirements and optimizing load conditions can improve efficiency.
- Temperature: Elevated temperatures can significantly affect the efficiency of a gear motor. Excessive heat can increase resistive losses, reduce lubrication effectiveness, and affect the magnetic properties of motor components. Proper cooling and thermal management techniques are essential to maintain optimal efficiency.
By considering these factors and implementing measures to minimize losses and optimize performance, the efficiency of a gear motor can be enhanced. Manufacturers often provide efficiency specifications for gear motors, allowing users to select motors that best meet their efficiency requirements for specific applications.

What is the significance of gear reduction in gear motors, and how does it affect efficiency?
Gear reduction plays a significant role in gear motors as it enables the motor to deliver higher torque while reducing the output speed. This feature has several important implications for gear motors, including enhanced power transmission, improved control, and potential trade-offs in terms of efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of the significance of gear reduction in gear motors and its effect on efficiency:
Significance of Gear Reduction:
1. Increased Torque: Gear reduction allows gear motors to generate higher torque output compared to a motor without gears. By reducing the rotational speed at the output shaft, gear reduction increases the mechanical advantage of the system. This increased torque is beneficial in applications that require high torque to overcome resistance, such as lifting heavy loads or driving machinery with high inertia.
2. Improved Control: Gear reduction enhances the control and precision of gear motors. By reducing the speed, gear reduction allows for finer control over the motor’s rotational movement. This is particularly important in applications that require precise positioning or accurate speed control. The gear reduction mechanism enables gear motors to achieve smoother and more controlled movements, reducing the risk of overshooting or undershooting the desired position.
3. Load Matching: Gear reduction helps match the motor’s power characteristics to the load requirements. Different applications have varying torque and speed requirements. Gear reduction allows the gear motor to achieve a better match between the motor’s power output and the specific requirements of the load. It enables the motor to operate closer to its peak efficiency by optimizing the torque-speed trade-off.
Effect on Efficiency:
While gear reduction offers several advantages, it can also affect the efficiency of gear motors. Here’s how gear reduction impacts efficiency:
1. Mechanical Efficiency: The gear reduction process introduces mechanical components such as gears, bearings, and lubrication systems. These components introduce additional friction and mechanical losses into the system. As a result, some energy is lost in the form of heat during the gear reduction process. The efficiency of the gear motor is influenced by the quality of the gears, the lubrication used, and the overall design of the gear system. Well-designed and properly maintained gear systems can minimize these losses and optimize mechanical efficiency.
2. System Efficiency: Gear reduction affects the overall system efficiency by impacting the motor’s electrical efficiency. In gear motors, the motor typically operates at higher speeds and lower torques compared to a direct-drive motor. The overall system efficiency takes into account both the electrical efficiency of the motor and the mechanical efficiency of the gear system. While gear reduction can increase the torque output, it also introduces additional losses due to increased mechanical complexity. Therefore, the overall system efficiency may be lower compared to a direct-drive motor for certain applications.
It’s important to note that the efficiency of gear motors is influenced by various factors beyond gear reduction, such as motor design, control systems, and operating conditions. The selection of high-quality gears, proper lubrication, and regular maintenance can help minimize losses and improve efficiency. Additionally, advancements in gear technology, such as the use of precision gears and improved lubricants, can contribute to higher overall efficiency in gear motors.
In summary, gear reduction is significant in gear motors as it provides increased torque, improved control, and better load matching. However, gear reduction can introduce mechanical losses and affect the overall efficiency of the system. Proper design, maintenance, and consideration of application requirements are essential to optimize the balance between torque, speed, and efficiency in gear motors.

What is a gear motor, and how does it combine the functions of gears and a motor?
A gear motor is a type of motor that incorporates gears into its design to combine the functions of gears and a motor. It consists of a motor, which provides the mechanical power, and a set of gears, which transmit and modify this power to achieve specific output characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a gear motor is and how it combines the functions of gears and a motor:
A gear motor typically consists of two main components: the motor and the gear system. The motor is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, generating rotational motion. The gear system, on the other hand, consists of multiple gears with different sizes and tooth configurations. These gears are meshed together in a specific arrangement to transmit and modify the output torque and speed of the motor.
The gears in a gear motor serve several functions:
1. Torque Amplification:
One of the primary functions of the gear system in a gear motor is to amplify the torque output of the motor. By using gears with different sizes, the input torque can be effectively multiplied or reduced. This allows the gear motor to provide higher torque at lower speeds or lower torque at higher speeds, depending on the gear arrangement. This torque amplification is beneficial in applications where high torque is required, such as in heavy machinery or vehicles.
2. Speed Reduction or Increase:
The gear system in a gear motor can also be used to reduce or increase the rotational speed of the motor output. By utilizing gears with different numbers of teeth, the gear ratio can be adjusted to achieve the desired speed output. For example, a gear motor with a higher gear ratio will output lower speed but higher torque, whereas a gear motor with a lower gear ratio will output higher speed but lower torque. This speed control capability allows for precise matching of motor output to the requirements of specific applications.
3. Directional Control:
Gears in a gear motor can be used to control the direction of rotation of the motor output shaft. By employing different combinations of gears, such as spur gears, bevel gears, or worm gears, the rotational direction can be changed. This directional control is crucial in applications where bidirectional movement is required, such as in conveyor systems or robotic arms.
4. Load Distribution:
The gear system in a gear motor helps distribute the load evenly across multiple gears, which reduces the stress on individual gears and increases the overall durability and lifespan of the motor. By sharing the load among multiple gears, the gear motor can handle higher torque applications without putting excessive strain on any particular gear. This load distribution capability is especially important in heavy-duty applications that require continuous operation under demanding conditions.
By combining the functions of gears and a motor, gear motors offer several advantages. They provide torque amplification, speed control, directional control, and load distribution capabilities, making them suitable for various applications that require precise and controlled mechanical power. Gear motors are commonly used in industries such as robotics, automotive, manufacturing, and automation, where reliable and efficient power transmission is essential.


editor by CX 2024-03-29
China Standard 12V 24V 48V Electric DC Brushed Worm Gear Motor with Worm Gearbox 10nm 20nm 30nm 50nm 60nm Power 50W 100W 150W 200W vacuum pump and compressor
Product Description
FAQ
Q: What’re your main products ?
A: We currently produce Brushed Dc Motors, Brushed DC Gear Motors, Planetary DC Gear Motors, Brushless
DCMotors, Stepper motors, AC Motors and High Precision Planetary Gear Box etc.
Q:How to select a suitable motor ?
A:lf you have motor pictures or drawings to show us, or you have detailed specs like voltage, speed, torque,
motor size, working mode of the motor, needed lifetime and noise level etc, please do not hesitate to let us know,
then we can recommend suitable motor per your request accordingly.
Q: Do you have a customized service for your standard motors ?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque and shaft size/shape.lf you need additional
wires/cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors or EMCwe can make it too.
Q: Do you have an individual design service for motors ?
A: Yes,we would like to design motors individually for our customers, but it may need some mold developingcost
and design charge.
Q: What’s your lead time ?
A:Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 15-30days, a bit longer for customized products.
But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | High Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Open Type |
| Number of Poles: | 2 |
| Samples: |
US$ 9.9/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can you explain the basic working principle behind a DC motor?
A DC (Direct Current) motor operates based on the fundamental principle of electromagnetic induction. It converts electrical energy into mechanical motion by utilizing the interaction between magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors. Here’s a detailed explanation of the basic working principle behind a DC motor:
1. Construction:
A DC motor consists of several key components:
- Stator: The stator is the stationary part of the motor and typically consists of permanent magnets or electromagnets that produce a fixed magnetic field.
- Rotor: The rotor is the moving part of the motor and is connected to the shaft. It contains coils or windings that carry the armature current.
- Armature: The armature is the core of the rotor that holds the armature windings. The windings are usually made of copper wire and are evenly spaced around the armature.
- Commutator: The commutator is a cylindrical ring attached to the rotor shaft. It consists of multiple segments, usually made of copper, that are insulated from each other.
- Brushes: The brushes are stationary contacts that make physical contact with the commutator segments. They are typically made of carbon or graphite and provide electrical connections to the armature windings.
2. Electromagnetic Induction:
When a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force due to the interaction between the magnetic field and the current. This phenomenon is described by the right-hand rule, where the direction of the force is perpendicular to both the current direction and the magnetic field direction.
3. Motor Operation:
When a DC motor is powered, a DC voltage is applied to the armature windings through the brushes and commutator. The current flowing through the armature windings creates a magnetic field around the windings. This magnetic field interacts with the fixed magnetic field produced by the stator, resulting in a force that causes the rotor to rotate.
4. Commutation:
The commutation process is crucial for the continuous rotation of the rotor in a DC motor. As the rotor spins, the brushes make contact with different commutator segments, effectively reversing the direction of the current in the armature windings at the appropriate timing. This reversal of current flow ensures that the torque generated in the armature windings is always in the same direction, allowing for continuous rotation of the rotor.
5. Speed Control:
The speed of a DC motor can be controlled by varying the applied voltage. Reducing the voltage results in a decrease in the magnetic field strength, which in turn decreases the force acting on the armature windings. This reduction in force leads to a decrease in the motor’s speed. Conversely, increasing the voltage increases the speed of the motor. Precise speed control can be achieved by using electronic circuits to regulate the voltage supplied to the motor.
6. Advantages and Applications:
DC motors offer several advantages, including:
- High starting torque, making them suitable for applications requiring high initial force.
- Excellent speed control capabilities, allowing for precise and adjustable speed regulation.
- Relatively simple construction and ease of maintenance.
- Wide range of sizes and power ratings, making them adaptable to various applications.
DC motors find extensive use in numerous applications, such as robotics, industrial automation, electric vehicles, appliances, and more.
By understanding the basic working principle behind a DC motor, one can appreciate its functionality and explore its applications in different fields.

Are there specific types of DC motors designed for different industries or applications?
Yes, there are specific types of DC (Direct Current) motors that are designed and optimized for various industries and applications. DC motors offer a wide range of performance characteristics, allowing them to be tailored to specific requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of the types of DC motors designed for different industries or applications:
1. Brushed DC Motors:
Brushed DC motors are commonly used in applications that require simple and cost-effective motor solutions. They are suitable for applications with lower efficiency requirements and where maintenance considerations are manageable. Some common industries and applications that use brushed DC motors include:
- Automotive: Power window mechanisms, windshield wipers, cooling fans, and seat adjustment systems.
- Consumer Electronics: Household appliances, toys, power tools, and personal care devices.
- Industrial Machinery: Conveyors, pumps, fans, and machine tools.
2. Brushless DC Motors:
Brushless DC motors are known for their higher efficiency, greater reliability, and precise control capabilities. They are widely used in industries and applications that demand higher performance and advanced control features. Some specific industries and applications that utilize brushless DC motors include:
- Automotive: Electric power steering systems, electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and HVAC systems.
- Aerospace and Defense: Actuators, robotics, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and missile systems.
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment: Centrifuges, pumps, robotics, and diagnostic devices.
- Industrial Automation: CNC machines, robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and precision motion control systems.
- Renewable Energy: Wind turbine generators, solar tracking systems, and energy storage systems.
3. High-Torque DC Motors:
High-torque DC motors are designed to provide substantial torque output at low speeds. They are commonly used in applications that require heavy lifting or high starting torque. Industries and applications that often utilize high-torque DC motors include:
- Material Handling: Cranes, hoists, winches, lifts, and elevators.
- Construction and Mining: Excavators, bulldozers, drilling rigs, and conveyor systems.
- Automotive: Electric vehicles, electric powertrains, and traction control systems.
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Thrusters, winches, and anchor handling systems.
4. Low-Voltage DC Motors:
Low-voltage DC motors are designed to operate at lower voltages, typically below 24 volts. They are commonly used in battery-powered applications and systems where safety or specific voltage requirements exist. Some industries and applications that utilize low-voltage DC motors include:
- Automotive: Automotive accessories, window actuators, and door locks.
- Robotics and Hobbyist Projects: DIY robots, RC vehicles, and model trains.
- Solar Power Systems: Solar tracking systems, solar panel actuators, and solar-powered water pumps.
- Home Automation: Automated blinds, curtains, and smart home devices.
These are just a few examples of the types of DC motors designed for different industries and applications. The versatility and adaptability of DC motors make them suitable for a wide range of uses, and manufacturers often offer customized motor solutions to meet specific requirements.

Are there innovations or emerging technologies in the field of DC motor design?
Yes, there have been several innovations and emerging technologies in the field of DC (Direct Current) motor design. These advancements aim to improve the performance, efficiency, reliability, and overall capabilities of DC motors. Here’s a detailed explanation of some notable innovations and emerging technologies in DC motor design:
1. Brushless DC Motors:
One significant advancement in DC motor design is the development and widespread adoption of brushless DC motors (BLDC motors). Unlike traditional DC motors that use brushes for commutation, BLDC motors employ electronic commutation through the use of permanent magnets and motor controller circuits. This eliminates the need for brushes, reducing maintenance requirements and improving overall motor efficiency and lifespan. BLDC motors offer higher torque density, smoother operation, better speed control, and improved energy efficiency compared to conventional brushed DC motors.
2. High-Efficiency Materials:
The use of high-efficiency materials in DC motor design has been an area of focus for improving motor performance. Advanced magnetic materials, such as neodymium magnets, have allowed for stronger and more compact motor designs. These materials increase the motor’s power density, enabling higher torque output and improved efficiency. Additionally, advancements in materials used for motor windings and core laminations have reduced electrical losses and improved overall motor efficiency.
3. Power Electronics and Motor Controllers:
Advancements in power electronics and motor control technologies have greatly influenced DC motor design. The development of sophisticated motor controllers and efficient power electronic devices enables precise control of motor speed, torque, and direction. These technologies have resulted in more efficient and reliable motor operation, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced motor performance in various applications.
4. Integrated Motor Systems:
Integrated motor systems combine the motor, motor controller, and associated electronics into a single unit. These integrated systems offer compact designs, simplified installation, and improved overall performance. By integrating the motor and controller, issues related to compatibility and communication between separate components are minimized. Integrated motor systems are commonly used in applications such as robotics, electric vehicles, and industrial automation.
5. IoT and Connectivity:
The integration of DC motors with Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and connectivity has opened up new possibilities for monitoring, control, and optimization of motor performance. By incorporating sensors, actuators, and connectivity features, DC motors can be remotely monitored, diagnosed, and controlled. This enables predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and real-time performance adjustments, leading to improved efficiency and reliability in various applications.
6. Advanced Motor Control Algorithms:
Advanced motor control algorithms, such as sensorless control and field-oriented control (FOC), have contributed to improved performance and efficiency of DC motors. Sensorless control techniques eliminate the need for additional sensors by leveraging motor current and voltage measurements to estimate rotor position. FOC algorithms optimize motor control by aligning the magnetic field with the rotor position, resulting in improved torque and efficiency, especially at low speeds.
These innovations and emerging technologies in DC motor design have revolutionized the capabilities and performance of DC motors. Brushless DC motors, high-efficiency materials, advanced motor control techniques, integrated motor systems, IoT connectivity, and advanced control algorithms have collectively contributed to more efficient, reliable, and versatile DC motor solutions across various industries and applications.


editor by CX 2024-03-26
China Good quality 63mm High Quality 12V 24V CZPT DC Worm Gear Motor with Encoder for Auto Door near me manufacturer
Product Description
63mm high top quality 12v 24v Micro DC Worm Gear Motor with encoder for Vehicle Doorway
DC WORM Equipment MOTOR 63ZYJ Sequence cocurrent long term magnetism deceleration electrical motor is the direct-current premanent magnetism deceleration electric powered motor which is composed by the 63ZYseries cocurrent permanet magnetism electrical motor and the worm gear reducer.
WORM Gear MOTOR SPECIFICATION:
Voltage: 12V 24V 30V 60V
Present: 5A 11A, 2.5A, 5.5A
MOTOR Information:
Torque: one hundred thirty~320mNm pace: 3000rpm Electricity: forty~100w
DECELERATION MOTOR Data:
Torque: 1~4.3N. M Speed: 1~430RPM
Motor knowledge can be adjusted in accordance to cusotomers ask for!
1.Creation Description
63mm diameter higher quality12V/ 24V DC worm equipment motor
1.measurement:Diameter 63mm
two.lifestyle time:5000 hours
three.content:copper or plastic
63mm diameter substantial high quality twelve/24V DC WORM Gear MOTOR
Motor Standard data:
Model: 63ZYT-WOG7080
Voltage: 12V, 24 V Torque:4.3 N.m Existing: 11 A
Pace: 94±10% rpm Motor energy:eighty five W
The specificaitons can be adjusted , such as voltage, pace , power , shaft diameter can be done it in accordance to customers ask for.
two.Production Circulation
three.Organization Details
In latest 10 many years, Derry has been dedicated to the manufacture of the motor items and the main items can be classified into the following collection, namely DC motor, DC gear motor, AC motor, AC gear motor, Stepper motor, Stepper gear motor, Servo motor and Linear actuator collection.
Our motor items are broadly utilized in the fields of aerospace business, automotive sector, monetary gear, family appliance, industrial automation and robotics, medical equipment, place of work equipment, packing CZPT and transmission industry, supplying clients reliable tailored answers for driving and controlling.
four.Our Companies
1). General Services:
two). Customization Service:
Motor specification(no-load speed , voltage, torque , diameter, sound, existence, screening) and shaft duration can be tailor-produced in accordance to customer’s demands.
5.Deal & Shipping
The Fundamentals of a Equipment Motor
The standard mechanism driving the equipment motor is the principle of conservation of angular momentum. The scaled-down the gear, the more RPM it addresses and the larger the gear, the a lot more torque it generates. The ratio of angular velocity of two gears is named the gear ratio. Furthermore, the very same basic principle applies to numerous gears. This indicates that the course of rotation of each and every adjacent equipment is constantly the reverse of the 1 it is connected to.
Induction worm gear motor
If you’re hunting for an electric motor that can produce large torque, an Induction worm equipment motor may be the proper option. This type of motor utilizes a worm equipment hooked up to the motor to rotate a major equipment. Due to the fact this variety of motor is more successful than other types of motors, it can be utilized in applications requiring enormous reduction ratios, as it is in a position to offer much more torque at a reduce velocity.
The worm equipment motor is created with a spiral shaft that is set into splines in yet another equipment. The speed at which the worm gear rotates is dependent on the torque developed by the primary equipment. Induction worm equipment motors are ideal suited for use in minimal-voltage apps this sort of as electric vehicles, renewable vitality methods, and industrial equipment. They appear with a extensive selection of electrical power-source possibilities, such as twelve-volt, 24-volt, and 36-volt AC electrical power supplies.
These kinds of motors can be used in numerous industrial configurations, which includes elevators, airport products, foods packaging amenities, and far more. They also create considerably less noise than other types of motors, which helps make them a well-liked choice for makers with minimal place. The effectiveness of worm gearmotors can make them an exceptional selection for purposes the place sounds is an concern. Induction worm gear motors can be compact and really high-torque.
While the Induction worm gear motor is most commonly used in industrial apps, there are other varieties of gearmotors available. Some kinds are far more efficient than others, and some are much more high-priced than other people. For your application, deciding on the proper motor and gearbox mix is critical to attaining the preferred result. You may locate that the Induction worm equipment motor is an exceptional choice for numerous apps. The benefits of an Induction worm gear motor cannot be overstated.
The DC gear motor is an superb option for high-conclude industrial purposes. This type of gearmotor is smaller sized and lighter than a common AC motor and can provide up to two hundred watts of torque. A equipment ratio of three to two can be found in these motors, which tends to make them best for a vast range of applications. A higher-quality DC equipment motor is a great decision for several industrial apps, as they can be very effective and provide a substantial stage of reliability.
Electric equipment motors are a flexible and widely utilized kind of electric motor. Even so, there are some apps that do not advantage from them, such as apps with higher shaft speed and low torque. Purposes such as supporter motors, pump and scanning equipment are examples of such high-speed and higher-torque calls for. The most crucial thought when deciding on a gearmotor is its effectiveness. Choosing the right dimensions will make certain the motor runs successfully at peak performance and will very last for several years.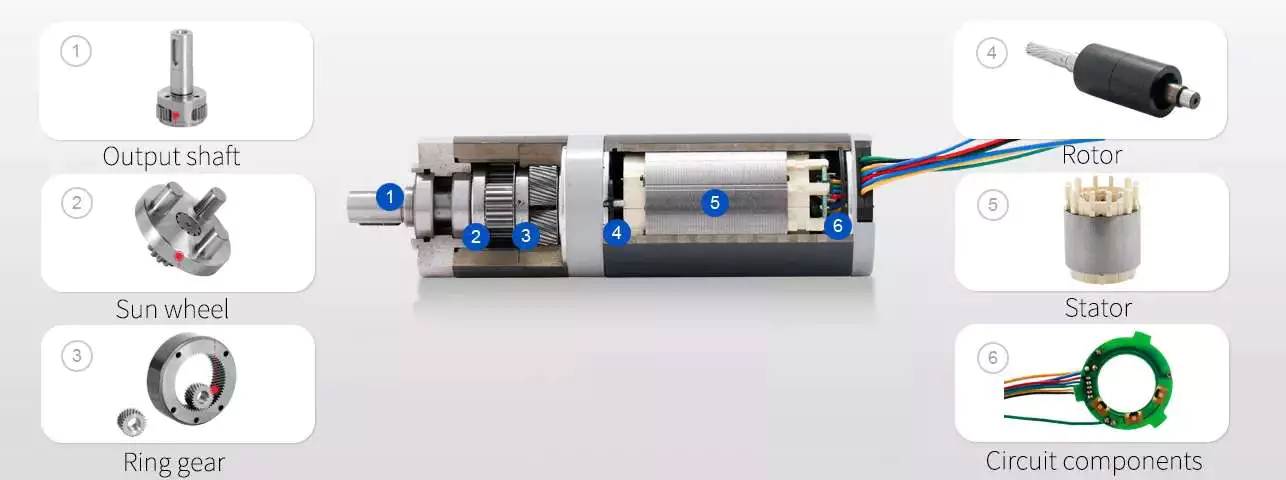
Parallel shaft helical equipment motor
The FC collection parallel shaft helical gearmotor is a compact, lightweight, and large-overall performance device that makes use of a parallel shaft construction. Its compact design and style is complemented by high transmission efficiency and high carrying capability. The motor’s materials is 20CrMnTi alloy metal. The device arrives with possibly a flanged input or bolt-on ft for installation. Its low sound and compact design and style make it an excellent option for a assortment of programs.
The helical gears are usually organized in two rows of 1 another. Every row includes one particular or much more rows of enamel. The parallel row has the teeth in a helical pattern, while the helical rows are lined up parallelly. In addition to this, the cross helical gears have a position contact style and do not overlap. They can be both parallel or crossed. The helical equipment motors can have any variety of helical pairs, each with a various pitch circle diameter.
The positive aspects of the Parallel Shaft Helical Gearbox include large temperature and strain dealing with. It is made by skilled specialists employing chopping-edge engineering, and is widely identified for its higher efficiency. It is available in a variety of technological specs and is custom made-manufactured to go well with personal demands. These gearboxes are durable and minimal-sound and function substantial dependability. You can expect to save up to forty% of your power by employing them.
The parallel shaft helical gear motors are designed to reduce the pace of a rotating portion. The nodular solid iron housing will help make the unit sturdy in hard environments, whilst the precision-machined gears provide peaceful, vibration-free of charge operation. These motors are obtainable in double reduction, triple reduction, and quadruple reduction. The ability ranges from .twelve kW to 45 kW. You can decide on from a broad selection of capacities, dependent on the size of your gearing needs.
The SEW-EURODRIVE parallel shaft helical gearmotor is a practical solution for room-constrained apps. The machine’s modular design and style enables for effortless mounting and a extensive selection of ambient temperatures. They are best for a variety of mechanical purposes, such as conveyors, augers, and much more. If you want a small footprint, the SEW-EURODRIVE parallel shaft helical equipment motor is the best answer for you.
The parallel shaft helical gears are beneficial for each substantial and minimal velocity applications. Parallel helical gears are also suited for lower velocity and lower duty apps. A very good illustration of a cross-helix equipment is the oil pump of an internal combustion motor. The two kinds of helical gears are highly reputable and supply vibration-totally free procedure. They are much more high priced than typical equipment motors, but offer much more longevity and efficiency.
Helical gear device
This helical equipment device is made to function under a range of demanding circumstances and can be used in a wide assortment of programs. Developed for lengthy daily life and large torque density, this gear device is offered in a variety of torques and gear ratios. Its design and development make it appropriate with a extensive assortment of essential mechanical methods. Frequent purposes include conveyors, material managing, steel mills, and paper mills.
Made for substantial-functionality apps, the Heidrive helical gear device supplies superior efficiency and value. Its revolutionary design and style permits it to perform properly below a broad selection of working problems and is extremely resistant to hurt. These equipment motors can be very easily combined with a helical gear unit. Their mixed electrical power output is a hundred Nm, and they have a large performance of up to ninety%. For far more data about the helical gear motor, speak to a Heidrive representative.
A helical gear device can be classified by its reference part in the regular plane or the turning airplane. Its middle gap is the same as that of a spur equipment, and its variety of teeth is the identical. In addition to this, the helical equipment has a lower axial thrust, which is one more critical attribute. The helical equipment unit is more effective at transferring torque than a spur equipment, and it is quieter, way too.
These units are created to manage huge masses. No matter whether you are utilizing them for conveyors, augers, or for any other application that requires high-pace motion, a helical equipment unit will supply optimum overall performance. A helical gear device from Flender can handle 400,000 jobs with a large degree of reliability. Its large efficiency and large resistance to load makes certain substantial plant availability. These equipment motors are offered in a assortment of measurements, from solitary-speed to multi-velocity.
PEC geared motors gain from a long time of style encounter and high high quality supplies. They are sturdy, tranquil, and offer superb overall performance. They are accessible in a number of configurations and are dimensionally interchangeable with other main brands. The gear motors are made as modular kits to reduce inventory. They can be equipped with further elements, these kinds of as backstops and followers. This helps make it easy to personalize your equipment motors and help save income even though decreasing fees.
One more kind of helical gears is the double helical gear. The double helical equipment device has two helical faces with a gap among them. They are much better for enclosed equipment techniques as they give increased tooth overlap and smoother efficiency. Compared to double helical gears, they are smaller sized and a lot more flexible than the Herringbone kind. So, if you happen to be searching for a equipment motor, a helical equipment unit may possibly be best for you.

